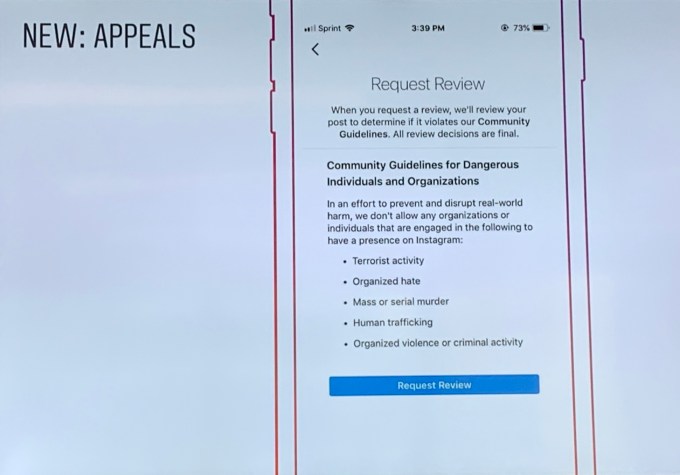
This array of unnatural images shows how conditions altered around NASA’s Mars corsair Opportunity as a outrageous dirt charge strong via Jun 2018. At left, a object appears blindingly splendid yet darkens as a dirt charge intensifies. At a distant right, a object is a small pinprick, with a dirt charge in full swing.
Huge Mars dirt storms like a one that killed NASA’s Opportunity corsair competence have helped to blow some of a Red Planet’s ancient H2O divided for good, researchers say.
In late May 2018, a dirt charge began hot adult around Opportunity, that had been exploring a Red Planet given Jan 2004. The dirt blocked sunlight’s trail to a ground, preventing a solar-powered drudge from recharging a batteries for weeks. Oppy never recovered, and NASA announced a corsair passed this past February.
But a charge didn’t only impact Opportunity’s digs nearby a Martian equator. By June, a maelstrom had grown into a tellurian monster, covering Mars with a cover of dust.
Related: Mars Dust Storm 2018: How It Killed a Opportunity Rover
Such planet-wide storms aren’t terribly rare; NASA booster also celebrated them in 1971, 1977 (twice), 1982, 1994, 2001 and 2007. (Opportunity and a twin, Spirit, managed to float out a 2007 storm, yet a one in 2018 was some-more powerful.) And these thespian events, that prominence how dry and dry Mars is today, competence have helped a world get that way, new investigate suggests.
Billions of years ago, Mars had a thick atmosphere and lots of glass water; Opportunity, Spirit and their newer, bigger corsair cousin, Curiosity, have found copiousness of justification to this outcome over a years. Indeed, scientists consider a low sea expected lonesome roughly 20% of a planet’s aspect in a ancient past.
Things began to change when Mars mislaid a tellurian captivating margin about 4 billion years ago. With this protecting separator gone, charged solar particles nude divided many of a planet’s atmosphere, and over time, Mars mislaid a ability to support glass H2O on a surface.
Global dirt storms competence have aided this process, a new investigate suggests. Researchers used a European-Russian ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) to lane a transformation of H2O fog in Mars’ atmosphere before and after a 2018 dirt storm.
TGO’s information prove that a maelstrom lofted H2O molecules most aloft into a Martian sky — from their standard altitude of about 12 miles (20 kilometers) to 50 miles (80 km) or some-more above a ground, a researchers said. Way adult there, where a atmosphere is really thin, solar deviation breaks detached H2O molecules into their basic hydrogen and oxygen atoms most some-more easily. These component components can afterwards be mislaid to space.
“When we move H2O to aloft tools of a atmosphere, it gets blown divided so most easier,” investigate co-author Geronimo Villanueva, a researcher during NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, said in a statement.
The study, that was published final month in a journal Nature, also reported a obscure result: TGO speckled no signs of methane in Mars’ atmosphere, even yet Curiosity has rolled by several plumes of a gas on a building of a 96-mile-wide (154 kilometers) Gale Crater.
Astrobiologists are penetrating to map Mars’ methane levels and know what’s producing it, since a gas competence be a pointer of biological activity on a Red Planet.
Researchers have been study a 2018 Mars dirt charge intensively, both to know how such events impact a planet’s meridian and to improved ready for destiny aspect missions. Dust storms poise a hazard to solar-powered rovers and landers — a existence highlighted by Opportunity’s fate. (Curiosity is nuclear-powered, so it was comparatively unaffected.)
Such storms can have knock-on effects, too. For example, Curiosity’s work shows that large dirt storms stop a arrangement of dirt devils — tornadoes of warm, dry atmosphere that can purify compromised solar panels.
“You need to be prepared to go a while before your subsequent dirt demon passes over and cleans we off,” Scott Guzewich, an windy scientist during NASA Goddard who’s a lead in a agency’s dirt charge investigation, pronounced in a same statement.
- In Photos: How NASA Said Goodbye to a Opportunity Rover on Mars
- Dust Storms Rage on Saturn Moon Titan, Just Like on Mars and Earth
- Mars’ Atmosphere: Composition, Climate Weather
Original essay on Space.com.